Z-Image-i2L (Image to LoRA): Instant Style Capture
In the rapidly evolving world of generative AI, the ability to customize image generation models is highly sought after. Typically, creating a Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) model to capture a specific style requires gathering a dataset, configuring a training script, and waiting for the fine-tuning process to complete.
Today, we are excited to introduce Z-Image-i2L, a model designed with a bold and experimental architecture that streamlines this process entirely. Instead of traditional training, this model treats the LoRA creation process as a direct inference task: Input an image, Output a LoRA.
In this post, we will explore the architecture behind Z-Image-i2L, demonstrate its capabilities in style retention, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to run it locally.
What is Z-Image-i2L?
i2L stands for "Image to LoRA." This project represents a continuation of Tongyi's experimental work, building upon the foundations of the previous Qwen-Image-i2L. While the core concept remains the same(predicting LoRA weights directly from visual input), it have been migrated the backbone to Z-Image.
The primary motivation behind this migration was to significantly enhance style retention. By leveraging the robust capabilities of the Z-Image framework, the i2L module can now analyze input images (or a small set of images) and generate a style-specific LoRA model in a matter of seconds. This allows for immediate style transfer and consistent character generation without the overhead of traditional training loops.
Achieving Best Results: Recommended Parameters
Because Z-Image-i2L operates differently from standard diffusion models, it requires specific inference settings to ensure the generated images are high-quality and free from artifacts.
Through the internal testing, we have identified a "Gold Standard" configuration. We strongly recommend using the following parameters when utilizing LoRAs generated by this model:
1. The "Positive-Only" Injection
This is the most critical trick. When applying the generated LoRA during inference, enable it only for the positive prompts and disable it for the negative prompts. This technique significantly improves image fidelity and prevents the style from bleeding into unwanted artifacts.
2. Parameter Settings
- CFG Scale:
4 - Sigma Shift:
8
3. Negative Prompts
To ensure clean outputs, a robust negative prompt is essential. You can use the following standard boilerplate:
English: "Yellowed, green-tinted, blurry, low-resolution, low-quality image, distorted limbs, eerie appearance, ugly, AI-looking, noise, grid-like artifacts, JPEG compression artifacts, abnormal limbs, watermark, garbled text, meaningless characters"
Style Transfer Showcase
The power of Z-Image-i2L lies in its ability to extract a cohesive style from just a few input images (or even a single image) and apply it to new prompts. Below are examples of how the model interprets different artistic directions.
(Note: All examples below were generated using a random seed of 0).
Style 1: Watercolor Painting
By inputting a reference of soft, blended watercolor art, the model generates a LoRA that applies this distinct brushwork to new subjects like cats, dogs, or portraits.
Input:
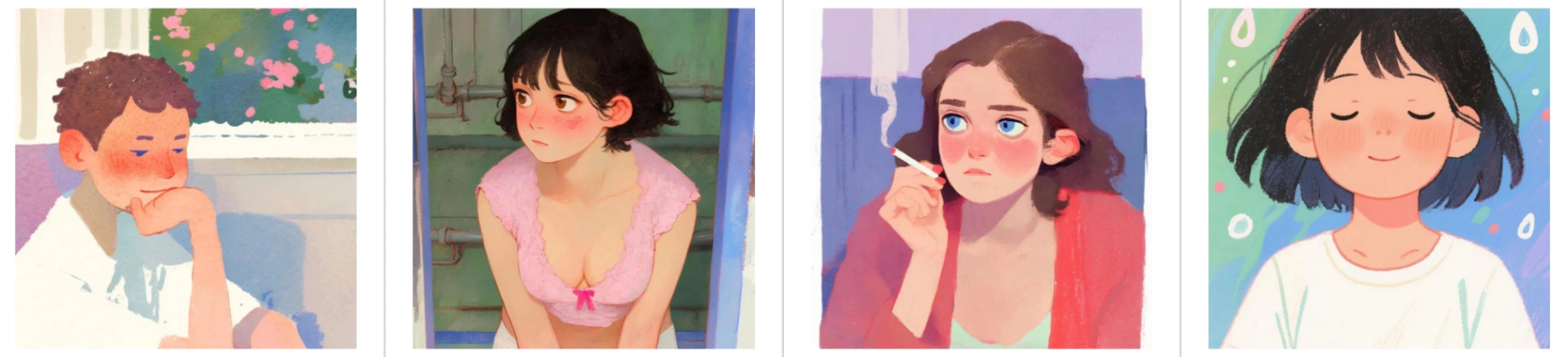

Output:
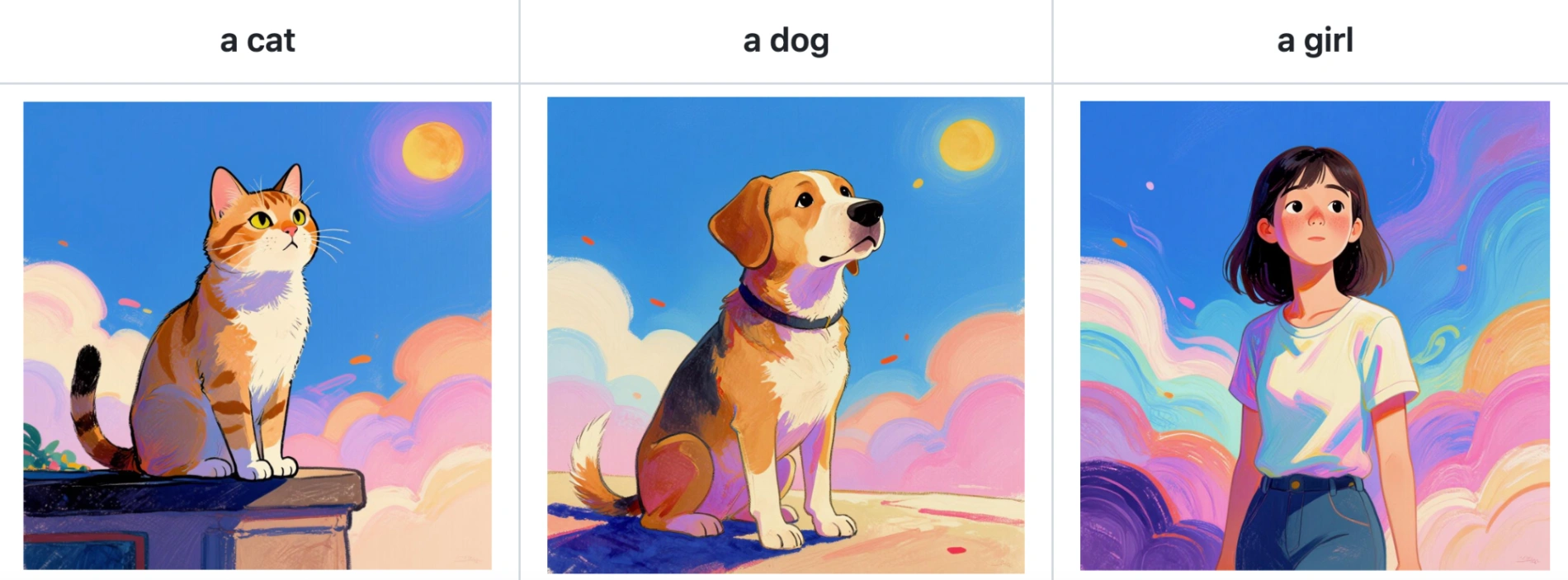
Style 2: Realistic Detail
When provided with high-fidelity photography, the generated LoRA focuses on texture, lighting, and photorealistic proportions.
Input:

Output:

Style 3: Colorful Blocks
The model can also capture abstract or graphic design styles, such as vibrant, flat color blocking.
Input:

Output:
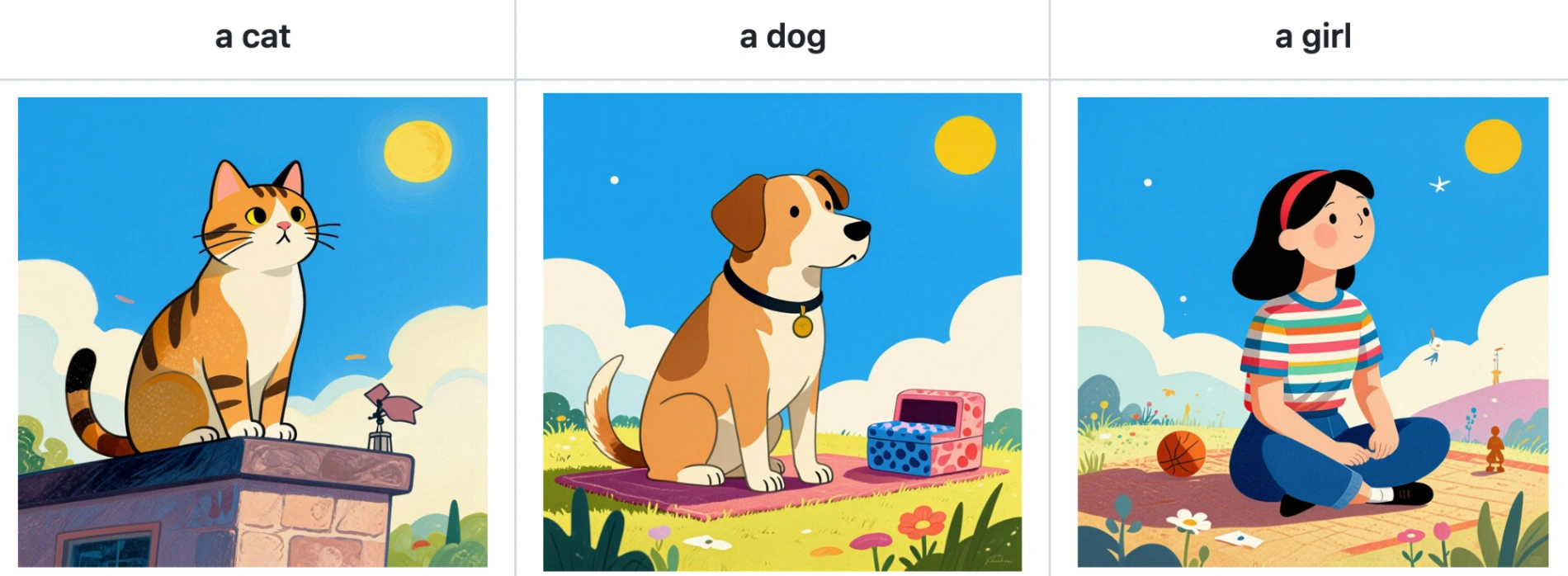
Style 4: Floral Aesthetics
Inputting images with soft floral motifs results in a LoRA that embeds flowers and gentle organic shapes into the background and foreground of the generated subjects.
Input:
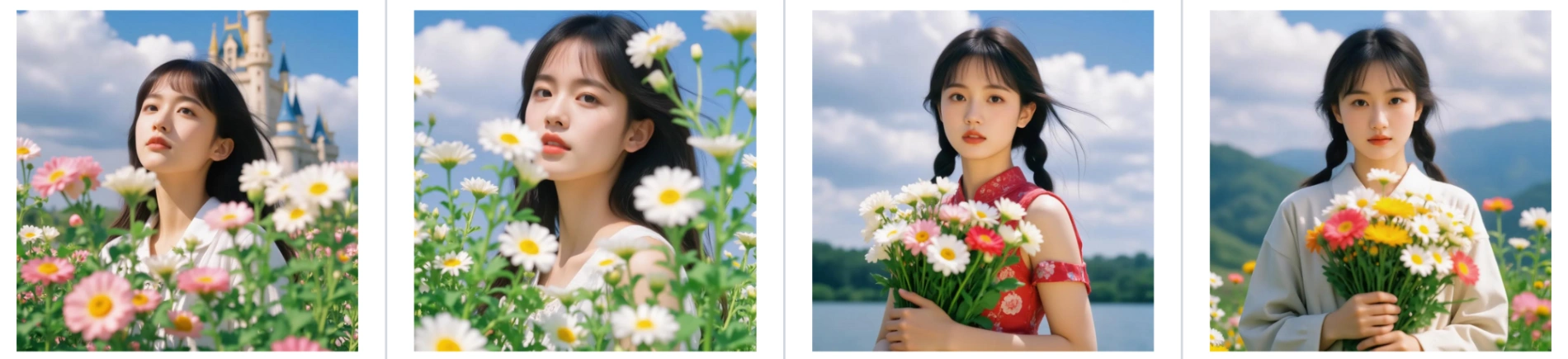

Output:

Style 5: Black & White Minimalist
For a stark, illustrative look, the model effectively strips away color and focuses on high-contrast linework.
Input:
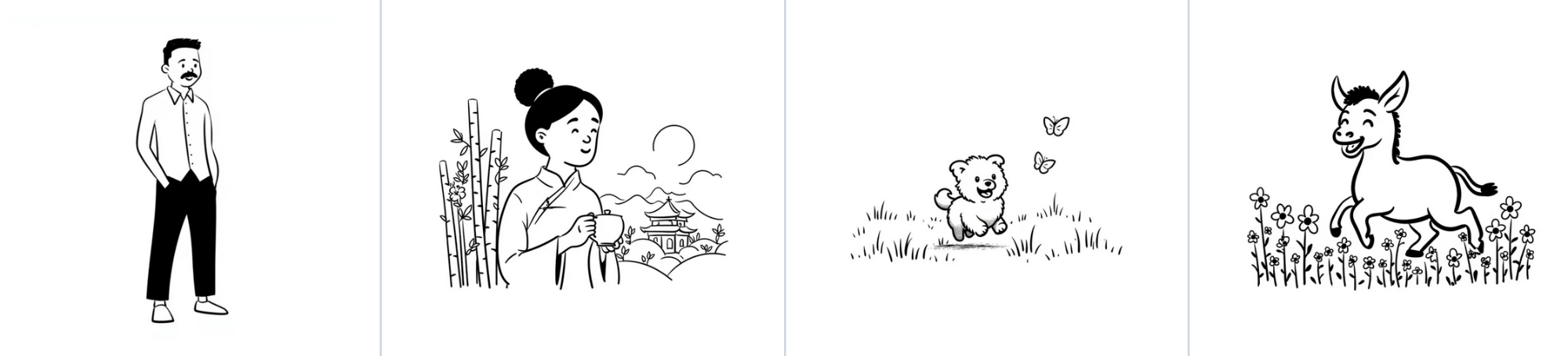

Output:

Style 6: Fantasy Worlds
Complex fantasy art styles with glowing effects and magical atmospheres are also preserved and transferred effectively.
Input:

Output:

Installation and Inference Guide
For developers and enthusiasts looking to run Z-Image-i2L locally, we have provided an implementation via DiffSynth-Studio.
Step 1: Installation
First, clone the repository and install the package in editable mode to ensure you have the latest dependencies.
git clone https://github.com/modelscope/DiffSynth-Studio.git
cd DiffSynth-Studio
pip install -e .
Step 2: Running the Model
The following Python script demonstrates the full workflow: loading the necessary encoders, processing input images into a LoRA, and then using that LoRA to generate a new image.
Z-Image-i2L utilize ZImageUnit_Image2LoRAEncode and ZImageUnit_Image2LoRADecode to handle the weight prediction.
from diffsynth.pipelines.z_image import (
ZImagePipeline, ModelConfig,
ZImageUnit_Image2LoRAEncode, ZImageUnit_Image2LoRADecode
)
from modelscope import snapshot_download
from safetensors.torch import save_file
import torch
from PIL import Image
# 1. Configuration for VRAM Optimization
# This config enables offloading to keep VRAM usage manageable during inference.
vram_config = {
"offload_dtype": torch.bfloat16,
"offload_device": "cuda",
"onload_dtype": torch.bfloat16,
"onload_device": "cuda",
"preparing_dtype": torch.bfloat16,
"preparing_device": "cuda",
"computation_dtype": torch.bfloat16,
"computation_device": "cuda",
}
# 2. Load the Pipeline and Sub-models
# We load the Z-Image backbone, Text Encoders, VAE, and the specific i2L modules.
pipe = ZImagePipeline.from_pretrained(
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device="cuda",
model_configs=[
ModelConfig(model_id="Tongyi-MAI/Z-Image", origin_file_pattern="transformer/*.safetensors", **vram_config),
ModelConfig(model_id="Tongyi-MAI/Z-Image-Turbo", origin_file_pattern="text_encoder/*.safetensors"),
ModelConfig(model_id="Tongyi-MAI/Z-Image-Turbo", origin_file_pattern="vae/diffusion_pytorch_model.safetensors"),
ModelConfig(model_id="DiffSynth-Studio/General-Image-Encoders", origin_file_pattern="SigLIP2-G384/model.safetensors"),
ModelConfig(model_id="DiffSynth-Studio/General-Image-Encoders", origin_file_pattern="DINOv3-7B/model.safetensors"),
# The star of the show: The i2L model
ModelConfig(model_id="DiffSynth-Studio/Z-Image-i2L", origin_file_pattern="model.safetensors"),
],
tokenizer_config=ModelConfig(model_id="Tongyi-MAI/Z-Image-Turbo", origin_file_pattern="tokenizer/"),
)
# 3. Prepare Input Images
# In this example, we download sample style assets from ModelScope.
snapshot_download(
model_id="DiffSynth-Studio/Z-Image-i2L",
allow_file_pattern="assets/style/*",
local_dir="data/Z-Image-i2L_style_input"
)
# Load 4 images that define the style we want to copy
images = [Image.open(f"data/Z-Image-i2L_style_input/assets/style/1/{i}.jpg") for i in range(4)]
# 4. Generate the LoRA (Image -> LoRA)
# The encoder processes the images into embeddings, and the decoder turns them into LoRA weights.
with torch.no_grad():
embs = ZImageUnit_Image2LoRAEncode().process(pipe, image2lora_images=images)
lora = ZImageUnit_Image2LoRADecode().process(pipe, **embs)["lora"]
# Optionally save the LoRA for later use
save_file(lora, "lora.safetensors")
# 5. Generate a New Image using the LoRA
prompt = "a cat"
negative_prompt = "Yellowed, green-tinted, blurry, low-resolution, low-quality image, distorted limbs, eerie appearance, ugly, AI-looking, noise, grid-like artifacts, JPEG compression artifacts, abnormal limbs, watermark, garbled text, meaningless characters"
# Notice: positive_only_lora=lora is crucial for quality!
image = pipe(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
seed=0,
cfg_scale=4,
num_inference_steps=50,
positive_only_lora=lora,
sigma_shift=8
)
image.save("image.jpg")
print("Image generated successfully.")
Conclusion
Z-Image-i2L represents a fascinating step forward in making AI art personalization more accessible and immediate. By bypassing the traditional training phase, it opens up new possibilities for real-time style switching and experimentation.
We humbly invite the community to try out this model, experiment with different inputs, and share your feedback. We are constantly learning and improving, and your insights help drive these technologies forward.
For an online demo, please visit our ModelScope Studio.
